Energy consumption is a critical aspect of modern society. The world’s population is growing, and with it, the demand for energy is also increasing. In this blog post, we will explore world energy consumption with facts and figures to understand the trends and challenges faced by the global community.
According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), the world’s energy consumption has been steadily increasing over the years, and it is expected to continue rising in the coming years. In 2020, the world’s energy consumption was 167,000 Tera Watt-hours (TWh), and it is expected to reach 204,000 TWh by 2040, a 22% increase.
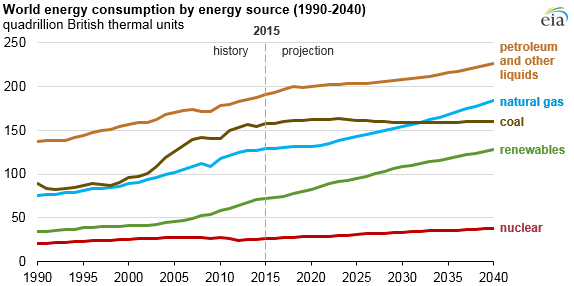
The primary source of energy for the world is fossil fuels, which include coal, oil, and natural gas. In 2020, fossil fuels accounted for 84% of the world’s energy consumption. However, the use of renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, hydro, and bioenergy, is also on the rise. In 2020, renewable energy accounted for 11% of the world’s energy consumption, up from 9% in 2015.

China is the world’s largest energy consumer, accounting for 24% of the world’s energy consumption in 2020. The United States is the second-largest energy consumer, accounting for 17% of the world’s energy consumption. India, Russia, and Japan round out the top five energy consumers, accounting for 5%, 4%, and 3% of the world’s energy consumption, respectively.
The transportation sector is the largest consumer of energy globally, accounting for 32% of the world’s energy consumption in 2020. The industrial sector is the second-largest consumer of energy, accounting for 28% of the world’s energy consumption. The residential and commercial sectors combined accounted for 22% of the world’s energy consumption in 2020.
The world’s energy consumption has a significant impact on the environment and contributes to climate change and air pollution. The burning of fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas releases large amounts of greenhouse gases, primarily carbon dioxide (CO2), into the atmosphere. These gases trap heat in the atmosphere, leading to global warming and climate change.
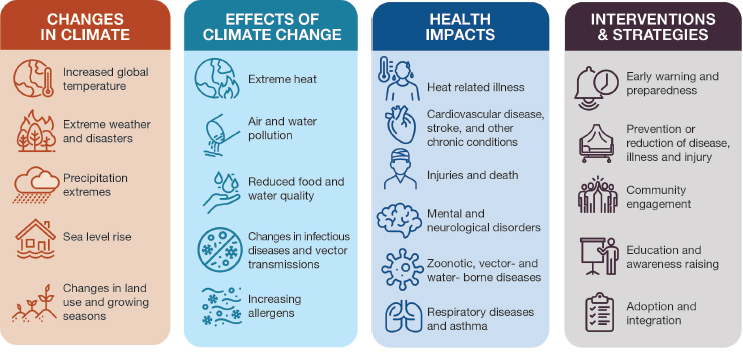
Climate change has serious consequences, including rising sea levels, more frequent and severe weather events, and changes in ecosystems that can impact human health, food security, and economic stability. In addition to contributing to climate change, the burning of fossil fuels also leads to air pollution, which can have harmful health effects, particularly for vulnerable populations such as children, the elderly, and people with respiratory illnesses.
Reducing energy consumption and transitioning to cleaner energy sources, such as renewable energy, can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution. Renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power produce little to no greenhouse gas emissions and have lower environmental impacts compared to fossil fuels.

In recent years, there has been a growing recognition of the need to address climate change and reduce carbon emissions. Many countries have set ambitious targets for reducing greenhouse gas emissions, and there is increasing investment in renewable energy and energy efficiency. However, there is still a long way to go, and it will require concerted efforts from governments, businesses, and individuals to transition to a low-carbon, sustainable energy system.
In conclusion, world energy consumption continues to rise, driven primarily by the use of fossil fuels. However, the use of renewable energy sources is also increasing, providing hope for a more sustainable future. As the world works to address climate change and reduce carbon emissions, reducing energy consumption and transitioning to cleaner energy sources will be critical in achieving these goals.